Difference between revisions of "User:Darkspace65"
Darkspace65 (Talk | contribs) (→Introduction) |
Darkspace65 (Talk | contribs) (→Prepare the joints) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Prepare the joints == | == Prepare the joints == | ||
[[File:bonestut02.png|left|frame|150x150px|PICTURE 3: Joints]] | [[File:bonestut02.png|left|frame|150x150px|PICTURE 3: Joints]] | ||
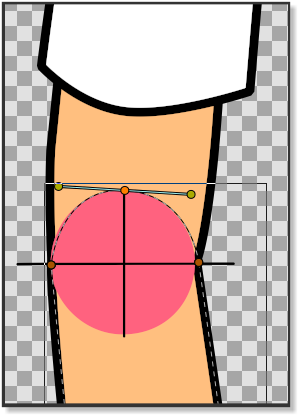
| − | Before we start rigging the arm we have to prepare it to make sure that the joints properly rotate. In ''picture 1'' we can see that the lower side of the upper arm is straight and does not have an outline, while the upper part of the lower arm has an outline that is curved. The bottom part of the lower arm does not have an outline and is also straight. The joint of the hand is also curved with an outline. To make sure that the joint parts of the arm rotate correctly, we made them with the help of a couple of crosshairs (picture 3). In ''picture 4'' and ''picture 5'' we can see how the horizontal crosshair line matches the straight line of the bottom of the upper arm and at the same time the outline of the circle of the crosshair matches the top curved outline of the lower arm. The same principle is applied to the hand and the bottom part of the lower arm. The crosshairs also mark the centre of the rotation point that will later be used when placing the bones. Before placing the bones we can align the {{l|Group Transformation Widget}} (press control and move the left corner vertex of the group transformation widget to move it.) of the '''lowerArm''' group and the '''hand''' group with the crosshairs of the elbow and the wrist to check the rotation. Don’t forget to bring the arm into its original position by pressing undo. (Don’t worry if the hand does not rotate with the elbow when you try the elbow joint.) | + | Before we start rigging the arm we have to prepare it to make sure that the joints properly rotate. In ''picture 1'' we can see that the lower side of the upper arm is straight and does not have an outline, while the upper part of the lower arm has an outline that is curved. The bottom part of the lower arm does not have an outline and is also straight. The joint of the hand is also curved with an outline. To make sure that the joint parts of the arm rotate correctly, we made them with the help of a couple of crosshairs (picture 3). In ''picture 4'' and ''picture 5'' we can see how the horizontal crosshair line matches the straight line of the bottom of the upper arm and at the same time the outline of the circle of the crosshair matches the top curved outline of the lower arm. The same principle is applied to the hand and the bottom part of the lower arm. The crosshairs also mark the centre of the rotation point that will later be used when placing the bones. Before placing the bones we can align the {{l|Group Transformation Widget}} (press control and move the left corner vertex of the group transformation widget to move it.) of the '''lowerArm''' group and the '''hand''' group with the crosshairs of the elbow and the wrist to check the rotation(pic.6). Don’t forget to bring the arm into its original position by pressing undo. (Don’t worry if the hand does not rotate with the elbow when you try the elbow joint.) |
| − | [[File:bonestut07.png|left|frame|150x150px|PICTURE 4: Joints align]] [[File:bonestut08.png|center|frame|150x150px|PICTURE 5: Joints align]] | + | [[File:bonestut07.png|left|frame|150x150px|PICTURE 4: Joints align]] [[File:bonestut08.png|center|frame|150x150px|PICTURE 5: Joints align]][[File:bonestut03.png|right|frame|150x150px|PICTURE 6: Testing joints]] |
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
Revision as of 20:10, 16 April 2015
Introduction
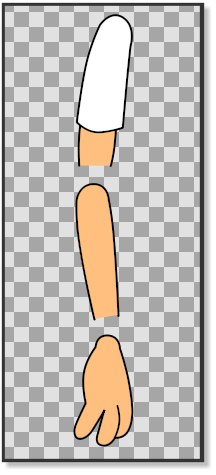
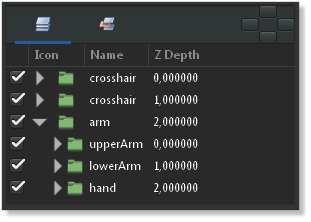
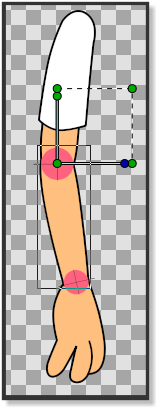
In this tutorial we are going to rig an arm with fixed joints using the skeleton layer and three bones. The arm consists of three parts: the upperArm, the lowerArm and the hand. (pic.1) Each part is grouped in its own layer and the three groups are again grouped in a layer that is called arm (pic.2).
Prepare the joints
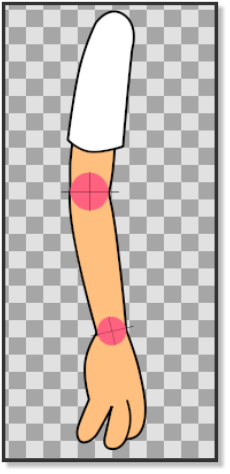
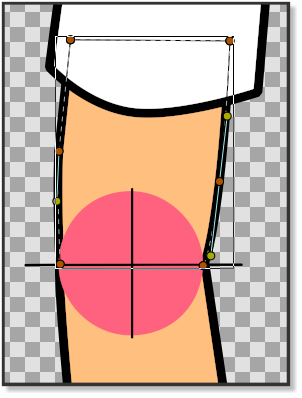
Before we start rigging the arm we have to prepare it to make sure that the joints properly rotate. In picture 1 we can see that the lower side of the upper arm is straight and does not have an outline, while the upper part of the lower arm has an outline that is curved. The bottom part of the lower arm does not have an outline and is also straight. The joint of the hand is also curved with an outline. To make sure that the joint parts of the arm rotate correctly, we made them with the help of a couple of crosshairs (picture 3). In picture 4 and picture 5 we can see how the horizontal crosshair line matches the straight line of the bottom of the upper arm and at the same time the outline of the circle of the crosshair matches the top curved outline of the lower arm. The same principle is applied to the hand and the bottom part of the lower arm. The crosshairs also mark the centre of the rotation point that will later be used when placing the bones. Before placing the bones we can align the Group Transformation Widget (press control and move the left corner vertex of the group transformation widget to move it.) of the lowerArm group and the hand group with the crosshairs of the elbow and the wrist to check the rotation(pic.6). Don’t forget to bring the arm into its original position by pressing undo. (Don’t worry if the hand does not rotate with the elbow when you try the elbow joint.)
Adding the bones
Now it’s time to add a skeleton layer that will provide the bones we need to rig the arm. Right-click on the Layers Panel and choose new layer/other/skeleton. A new skeleton layer will appear in the Layers Panel alongside with a small bone in the canvas. (pic. Arm04 and layers03) Put the skeleton layer above the arm group. To know more about the skeleton layer and bones click here. The green vertex above the blue vertex of the bone is used to move the bone in place and is also its centre of rotation. The blue vertex is used to rotate the bone. The green vertex under the blue one is used to stretch the bone. The first bone is the parent bone and should be moved toward the shoulder and stretched so that it almost reaches the outlines of the first crosshair of the elbow. Right click on any of the vertices of the parent bone and select create child bone. Move the rotation point of the child bone so that it matches the crosshair of the elbow and stretch it until it almost reaches the crosshair of the wrist. Right click on any of the vertices of the child bone and create another child bone. Move the centre of the second child bone so that it matches the crosshair of the wrist. Stretch the bone until it reaches the end of the fingers.
Attaching the bones
Now that the skeleton is in place we have to attach the bones to the parts of the arm. In the layers panel click on the upper arm group, right-click and select all the children. Then press CtrlA in the canvas window. With everything in the upper arm group highlighted, Ctrl click on the parent bone in the canvas window and right-click on any of the vertices of the parent bone and click link to bone. The upper arm group is now linked to the parent bone. Go the layers panel again and select the lower arm group. Right-click and select all the children. Press CtrlA in the canvas window and Ctrl-click on one of the bones. Then right-click on any of the vertices of the first child bone and select "Link to bone". The lowerArm group is now linked to the second child bone. In the Layers Panel select all the children of the hand layer and press CtrlA in the canvas window. Ctrl click on any bone and then right-click on any of the vertices of the second child bone and select link to bone. The hand is now linked to the second child bone and the entire skeleton is now linked to the arm.