Blur Layer
Contents
About Blurs
Blur is a graphical effect that aims to imitate an unfocused image. In a photography context blur can occur when the focal point of the lens is not at the right position of the target of the photograph. Also blur can have other origins. Blurs can happen as the result of a poor exposure during its recording (too long exposure time for a large movement of the object or a high movement of the recorder). Also blurring occurs when you use a very wide aperture (f4). In that case the objects that are out of focus are very blurred compared to the situation where the aperture is fully closed (f22).
In a graphical context, blurs are effects that imitate those situations (with more or less success).
Specific Parameters
The specific parameters for the Blur Layer are:
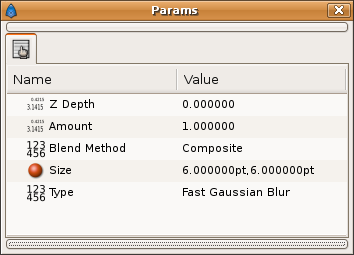
|
Size
The Size parameter controls how big is the blur. Depending on that value the blur can have different effects. If you increase so much the blur value the render time increases a lot so be careful.
This parameter is a compound value of two real numbers (x and y). Everyone indicate how big is the blur in its direction (x or y).
See the samples to get an idea of the variation on the sizes.
Types
There are 5 types of blur in synfig:
Samples
Here there are some samples of Blurs.
Fast Gaussian
| Fast Gaussian Blur | |

|

|
Box
| Box Blur | |

|

|
Cross Hatch
| Cross Hatch Blur | |

|

|
Disc
| Disc Blur | |

|

|
Gaussian
| Gaussian Blur | |

|

|
| Fast Gaussian Blur over all the layers |

|
See also
- Radial Blur with a radial control of the size of the blur.
- Motion Blur a type of blur that want to simulate a motion blur (the one that happen when the object's movement is faster than the exposition time). It is controlled by a single parameter called "Apertue".