Difference between revisions of "Convert"
m (→String) |
m (→Random: Remove subversion note. It is included in 0.61.08) |
||
| Line 257: | Line 257: | ||
=== Random === | === Random === | ||
| − | |||
Converting a parameter to "Random" adds five sub-parameters, the first of which is the same type as the converted parameter: | Converting a parameter to "Random" adds five sub-parameters, the first of which is the same type as the converted parameter: | ||
Revision as of 00:02, 30 June 2008
Right-clicking on a value in the Parameters dialog brings up a context menu which has a sub-menu called "Convert". The "Convert" menu allows you to specify that the parameter should be controlled automatically in various ways. Depending on the type of the parameter the Convert menu will contain different options.
To convert the value back to its original type, select "Disconnect" from its context menu.
Contents
- 1 Convert Types
- 1.1 Add
- 1.2 Angle String
- 1.3 aTan2
- 1.4 BLine
- 1.5 BLine Tangent
- 1.6 BLine Vertex
- 1.7 BLine Width
- 1.8 Composite
- 1.9 Cos
- 1.10 Dot Product
- 1.11 Duplicate
- 1.12 Dynamic List
- 1.13 Exponential
- 1.14 From Integer
- 1.15 Gradient Color
- 1.16 Gradient Rotate
- 1.17 Int String
- 1.18 Joined List
- 1.19 Linear
- 1.20 Radial Composite
- 1.21 Random
- 1.22 Range
- 1.23 Real String
- 1.24 Reciprocal
- 1.25 Reference
- 1.26 Repeat Gradient
- 1.27 Reverse Tangent
- 1.28 Scale
- 1.29 Segment Tangent
- 1.30 Segment Vertex
- 1.31 Sine
- 1.32 Step
- 1.33 Example
- 1.34 Stripes
- 1.35 Subtract
- 1.36 Switch
- 1.37 Time Loop
- 1.38 Time String
- 1.39 Timed Swap
- 1.40 Two-Tone
- 1.41 Vector Angle
- 1.42 Vector Length
- 1.43 Vector X
- 1.44 Vector Y
- 2 Which Value Types can use which Convert Types?
- 3 Compatibility
Convert Types
Add
Converting a parameter to "Add" adds three sub-parameters, the first two of which are the same type as the parameter itself:
- <param> "LHS"
- <param> "RHS"
- real "Scalar"
The "Add" conversion can be used with parameters of type angle, color, gradient, integer, real, time, and vector.
The resulting value is:
(LHS + RHS) * Scalar
Angle String
Converting an string-valued parameter to "Angle String" adds four sub-parameters:
- angle "Angle"
- integer "Width"
- integer "Precision"
- bool "Zero Padded"
The resulting value a string containing the value of "Angle" (in degrees) formatted as a string with a minimum width "Width", with "Precision" decimal places. If "Zero Padded" is true, it will be left-padded with "0" characters.
aTan2
Converting an angle-valued parameter to "aTan2" adds two sub-parameters:
- real "X"
- real "Y".
The resulting value is:
atan2(y,x)
ie. atan(y/x) but without an error when x is 0. The value is the angle between the x axis and the vector (x,y).
BLine
Converting a list parameter to "BLine" doesn't seem to change anything. Perhaps that's the default type for lists of vertices, such as are found in outlines and regions?
BLine Tangent
Converting a angle, real (since SVN r1862), or vector parameter to "BLine Tangent" adds six sub-parameters:
- bline "BLine"
- bool "Loop"
- real "Amount"
- angle "Offset" (since SVN r1863)
- real "Scale" (since SVN r1863)
- bool "Fixed Length" (since SVN r1863)
Amount is a number between 0 and 1, defining the distance along the given bline. The resulting value for the whole parameter is the tangent to the bline, at the given point along the bline, optionally rotated and scaled according to the "Offset", "Scale", and "Fixed Length" parameters.
"Offset" is an angle used to give the tangent an extra rotation before returning it. If "Fixed Length" is true, the tangent is then scaled to have a length equal to "Scale". Otherwise the tangent is multiplied by "Scale".
If a vector was converted the result is the tangent itself. If an angle was converted, the result is the angle of the tangent to the horizontal, and if a real was converted, the result is the length of the tangent.
This tutorial gives an example of the use of this convert type.
BLine Vertex
Converting a vector parameter to "BLine Vertex" adds three sub-parameters:
- bline "BLine"
- bool "Loop"
- real "Amount"
Amount is a number between 0 and 1, defining the distance along the given bline. The resulting value for the whole parameter is a vector giving the position of the given point along the bline.
This tutorial gives an example of the use of this convert type.
BLine Width
Converting a real parameter to "BLine Width" adds three sub-parameters:
- bline "BLine"
- bool "Loop"
- real "Amount"
- real "Scale" (since SVN r1872)
Amount is a number between 0 and 1, defining the distance along the given bline. The resulting value for the whole parameter is the width of the bline at the given point along it, multiplied by the "Scale" parameter.
Composite
Converting a blinepoint parameter to "Composite" adds six sub-parameters:
- vector "Vertex"
- real "Width"
- real "Origin"
- bool "Split Tangents"
- vector "Tangent 1"
- vector "Tangent 2"
Converting a color parameter to "Composite" adds four real-valued sub-parameters:
- real "Red"
- real "Green"
- real "Blue"
- real "Alpha"
Converting a segment parameter to "Composite" adds four vertex sub-parameters:
- vertex "Vertex 1"
- vertex "Tangent 1"
- vertex "Vertex 2"
- vertex "Tangent 2"
Converting a vector parameter to "Composite" adds two real-valued sub-parameters:
- real "X-Axis"
- real "Y-Axis"
The resulting value is a blinepoint, color, segment, or vector made by combining the component parts.
Cos
Converting a real-valued parameter to "Cos" adds two sub-parameters:
- angle "Angle"
- real "Amplitude".
The resulting value is:
Amplitude * cos(Angle)
Dot Product
Converting a real or angle parameter to a "Dot Product" adds two sub-parameters:
- vector "LHS"
- vector "RHS"
If the converted value is an angle, the return value is the angle between the two vectors:
return = acos((LHS · RHS) / (|LHS| * |RHS|))
If the converted value is a real, the result value is the dot product of the two vectors:
return = LHS · RHS = |LHS| * |RHS| * cos(alpha)
(where alpha is the angle between LHS and RHS).
Duplicate
This ValueNode type is only used by the Duplicate Layer. It never appears in the Convert menu. It is used to control the range of the Index in the Duplicate Layer (q.v.).
The "Duplicate" ValueNode type has 3 real-valued sub-parameters:
- real "From"
- real "To"
- real "Step"
The value of the ValueNode varies from the value of "From" to the value of "To" in steps of size "Step". The sign of "Step" is ignored. If From<To the steps are positive, else they're negative.
Dynamic List
Converting a list parameter to "Dynamic List" seems to replace each of the "Vertex NNN" sub-parameters with "Item NNN" parameters which can't be expanded, but can be exported.
Exponential
Converting a real parameter to "Exponential" adds two sub-parameters:
- real "Exponent"
- real "Scale"
The resulting value is the result raising the mathematical constant 'e' to the power of Exponent, and scaling the result by Scale. That is, it returns:
Scale * e^Exponent
This is useful for tracking layers which have been zoomed, since the Zoom layer scales by e^(zoom factor).
See this video for an example of the use of this convert type.
From Integer
This is currently disabled. It converts an integer to one of several types.
Gradient Color
Converting a color parameter to "Gradient Color" adds two sub-parameters:
- gradient "Gradient"
- real "Index"
The resulting value is a color taken from the gradient at the given index position. Index 0 corresponds to the left of the gradient; index 1 corresponds to the right of the gradient.
Gradient Rotate
Converting a gradient parameter to "Gradient Rotate" adds two sub-parameters:
- gradient "Gradient"
- real "Offset"
The resulting value is a gradient based on the "Gradient" parameter, but shifted left (for negative values) or right, according to the value of the "Offset" parameter. An offset of 1.0 will shift the gradient by its entire visible width. Values shifted off the left or right edge aren't lost - they aren't visible in the gradient as it's displayed in the parameters dialog, but they will still be used when rendering (depending on parameters such as 'Loop' and 'Zigzag', which can cause gradients to be looped between their their left and right edges, rather than using the non-displayed parts).
Int String
Converting an string-valued parameter to "Int String" adds three sub-parameters:
- integer "Int"
- integer "Width"
- bool "Zero Padded"
The resulting value a string containing "Int" formatted as a string with a minimum width "Width". If "Zero Padded" is true, it will be left-padded with "0" characters.
Joined List
Converting a string parameter to be 'Joined List' adds four sub-parameters:
- list "Strings"
- string "Before"
- string "Separator"
- string "After"
The result is a string containing the value of "Before", followed by all the strings in the "Strings" list, with the value of "Separator" between each pair, followed by the value of "After".
Linear
Converting an angle parameter to be 'Linear' adds two angle sub-parameters:
- angle "Rate"
- angle "Offset"
Converting a color parameter to be 'Linear' adds two angle sub-parameters (since svn r617):
- color "Rate"
- color "Offset"
Converting an integer parameter to be 'Linear' adds two angle sub-parameters (since svn r617):
- integer "Rate"
- integer "Offset"
Converting a real parameter to be 'Linear' adds two real-valued sub-parameters:
- real "Rate"
- real "Offset"
Converting a time parameter to be 'Linear' adds two time sub-parameters:
- time "Rate"
- time "Offset"
Converting a vector parameter to be 'Linear' adds two vector sub-parameters:
- vector "Slope"
- vector "Offset"
The parameter's value will change linearly over time, starting with the value specified by "Offset" at time zero, and increasing by the value specified by "Rate" (or "Slope", in the case of vector parameters) every second.
The resulting value for vector parameters is:
Offset + Slope*time
and for the other 5 types of parameter it is:
Offset + Rate*time
Radial Composite
Converting a color to "Radial Composite" adds four sub-parameters:
- real "Luma"
- real "Saturation"
- angle "Hue"
- real "Alpha"
Converting a vector to "Radial Composite" adds two sub-parameters:
- real "Radius"
- angle "Theta"
For color parameters, the resulting value is the color with the given lima, saturation, hue, and alpha amounts.
For vector parameters, the resulting value is the point reached by traveling a distance "Radius" from the origin, in the distance given by the angle "Theta".
Random
Converting a parameter to "Random" adds five sub-parameters, the first of which is the same type as the converted parameter:
- <param> "Link"
- real "Radius"
- integer "Seed"
- real "Animation Speed"
- integer "Interpolation"
"Random" can be used on angles, colors, integers, reals, times, and vectors.
It is used to cause a parameter's value to vary randomly over time, around a central value:
- "Link" provides the central value.
- "Radius" defines the maximum random difference.
- "Seed" seeds the random number generator
- "Animation Speed" defines how often a new random value is chosen (in choices per second)
- "Interpolation" determines how the value is interpolated from one random choice to the next. Possible values are:
- 0 - no interpolation; the value jumps from one value to the next
- 1 - linear interpolation
- 2 - cosine
- 3 - spline
- 4 - cubic (the default); uses Catmull-Rom spline interpolation
The "Interpolation" sub-parameter should really be a drop-down menu, rather than an integer field, but that isn't yet implemented.
Range
Converting a parameter to "Range" adds three sub-parameters, all the same type as the parameter itself:
- <param> "Min"
- <param> "Max"
- <param> "Link"
"Range" can be used on angles, integers, reals, and times.
It is used to limit the value of the linked parameter to be between Min and Max.
The resulting value is:
Min (if Link < Min) Max (if Link > Max) Link (otherwise)
Real String
Converting a string parameter to "Real String" adds four sub-parameters:
- real "Real"
- int "Width"
- int "Precision"
- bool "Zero Padded"
The result is a string formatted to contain the given value "Real". "Width" specifies the minimum field width, "Precision" specifies the number of decimal places and "Zero Padded" specifies whether to pad with zeros on the left hand side.
For example, with Real=3.1415, Width=6, Precision=2, and ZeroPadded=true, we get:
"003.14"
(6 characters long, 2 decimal places, and padded with zeros on the left).
Reciprocal
Converting a real-valued parameter to "Reciprocal" adds three sub-parameters:
- real "Link"
- real "Epsilon".
- real "Infinite".
The resulting value is:
1/Link (Link <= -epsilon or epsilon <= Link) Infinite (if 0 <= Link < epsilon) -Infinite (if -epsilon < Link < 0)
The epsilon and infinite parameters are only needed to prevent division by zero. For regular operation the resulting value is simply the reciprocal of Link.
Reference
Converting a parameter to "Reference" adds a single sub-parameter called "Link". The "Link" parameter is the same type as the parameter being converted.
It doesn't seem to do anything at all, other than adding an extra parameter. Whatever value is put into "Link" becomes the value of the parameter being converted.
The only use for this conversion type I can think of is the following:
- you know that point A should follow point B, so you export point B and connect point A to it
- you're not yet sure exactly how point B should move, so you experiment with different conversion types for point B
- changing the conversion type for point B breaks the connection you made in the first step
- converting point B to be a reference, and then experimenting with different conversions in its "Link" parameter allows point A to connect to point B and for the connection to remain in place while you experiment in the "Link" parameter
The resulting value is:
Link
Repeat Gradient
Converting a gradient parameter to "Repeat Gradient" adds seven sub-parameters:
- gradient "Gradient"
- integer "Count"
- real "Width"
- bool "Specify Start"
- bool "Specify End"
- color "Start Color"
- color "End Color"
The resulting value is a gradient containing "Count" equally spaced, equally wide copies of gradient "Gradient". Each copy has "Gradient" going forwards and then backwards. "Width" specifies relative width of the forward copy, with a width of 0 or less meaning only the backward copy is used, and a width of 1 or more meaning only the forward copy is used. A value of 0.5 will result in the forward and reverse copies of "Gradient" being the same width.
If "Specify Start" is checked then "Start Color" will be inserted at the beginning of the new gradient, otherwise the beginning of "Gradient" will be used as the beginning of the new gradient.
If "Specify End" is checked then "End Color" will be appended to the end of the new gradient, otherwise the end of "Gradient" will be used as the end of the new gradient.
Here's an example of a repeated gradient - the radiating green/yellow lines are a repeated gradient, applied to a perpendicular curve gradient. This gradient was repeated with a width of 0.5, meaning it is used backwards and forwards the same amount:
and here's the resulting image, along with the .sif file:
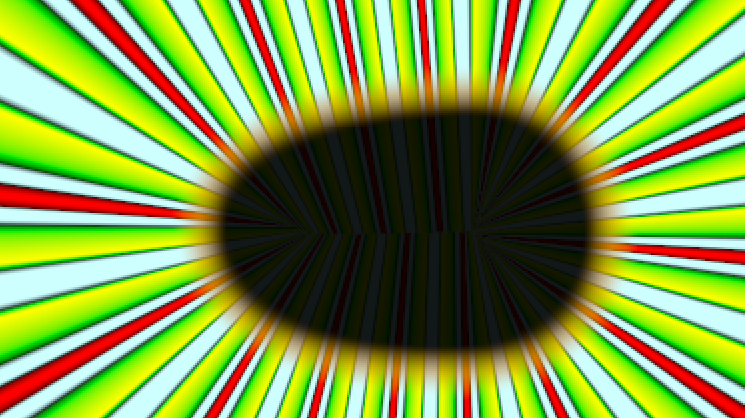 File:Repeat-gradient-valuenode.sif
File:Repeat-gradient-valuenode.sif
Reverse Tangent
Converting a blinepoint parameter to "Reverse Tangent" adds two sub-parameters: one called "Reference" of type BLinePoint, and a boolean parameter called "Reverse".
- BLinePoint "Reference"
- bool "Reverse"
"Reverse Tangent" can only be used on blinepoints.
The resulting value is the same as the reference BLinePoint, but with its tangents switched over. This is useful when attempting to link the verticies of a region to the vertices of an outline when the region and the outline were drawn in opposite directions, and so tangent1 of an outline vertex needs to be linked to tangent2 of the region vertex, and vice versa.
Scale
Converting a parameter to "Scale" adds two sub-parameters: one called "Link", of the same type as the parameter itself, and a real-valued parameter called "Scalar".
- <param> "Link"
- real "Scalar"
"Scale" can be used on angles, colors, integers, reals, times, and vectors.
The resulting value is:
Link * Scalar
Segment Tangent
Converting a vector parameter to "Segment Tangent" adds two sub-parameters:
- segment "Segment"
- real "Amount"
Amount is a number between 0 and 1, defining the distance along the given segment. The resulting value for the whole parameter is the tangent to the segment, at the given point along the segment.
Segment Vertex
Converting a vector parameter to "Segment Vertex" adds two sub-parameters:
- segment "Segment"
- real "Amount"
Amount is a number between 0 and 1, defining the distance along the given segment. The resulting value is the vertex at the given point along the segment.
Sine
Converting a real-valued parameter to "Sine" adds two sub-parameters:
- angle "Angle"
- real "Amplitude".
The resulting value is:
Amplitude * sin(Angle)
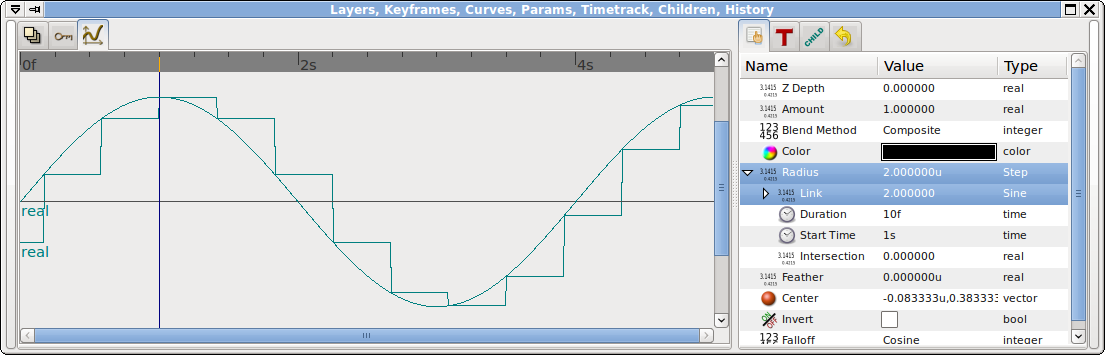
Step
Converting an angle, color, integer, real, time, or vector parameter to be 'Step' adds four sub-parameters:
- <param> "Link"
- time "Duration"
- time "Start Time"
- real "Intersection"
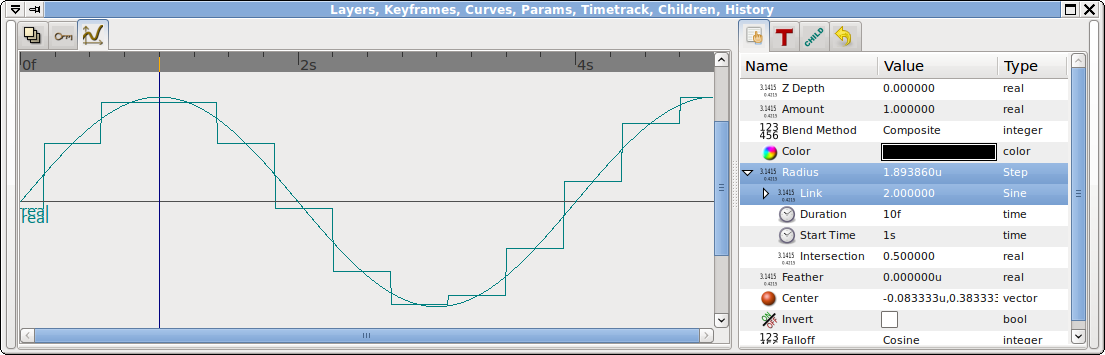
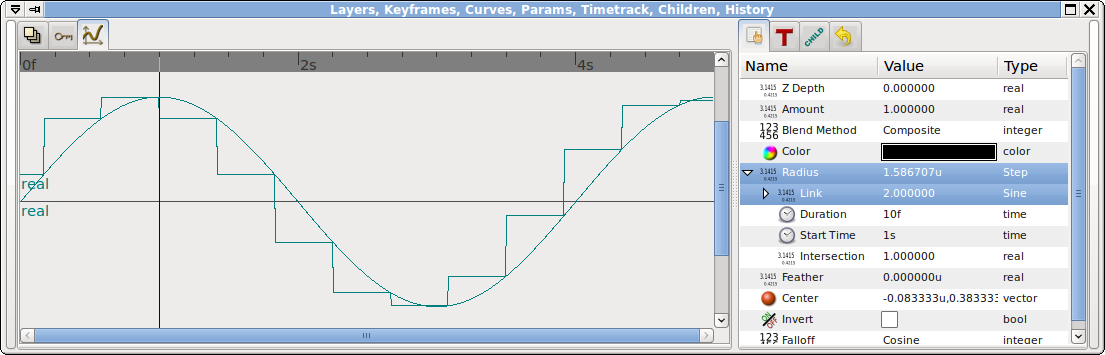
The parameter's value will change in steps. Each step is "Duration" seconds long. The steps start at times "Start Time", "Start Time"+"Duration", etc. The value of the valuenode is the value of "Link" at some time. "Intersection" determines which time is used. An "Intersection" of 0.0 means that the value of "Link" at the start of the step should be used. An "Intersection" of 0.5 (the default) means to use the value of "Link" at the middle of the step, etc.
The resulting value at time Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://api.formulasearchengine.com/v1/":): {\displaystyle T} is:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://api.formulasearchengine.com/v1/":): {\displaystyle Link \Bigg ( \Bigg ( Duration \cdot \left ( \left \lfloor \frac{T - Start\ Time}{Duration} \right \rfloor + Intersection \right ) \Bigg ) + Start \ Time \Bigg )}
Example
"Link" is a sine wave. "Duration" is 10f (the frame rate is 24 fps). "Start Time" is 1s.
So one step starts at 1s, and others start at 0s 14f, 0s 4f, 1s 10f, etc.
This is the sine wave:
And this is the effect of the Step valuenode on it, with an "Intersection" of 0.0. Notice that at time 0s, the step has a negative value -- that step runs from -6f to 4f, and so its value is the value of Link at time -6f. These images were created in The Gimp - it's not currently possible to view two curves at the same time in Synfig Studio.
Here it is with an "Intersection" of 0.5:
and here, with an "Intersection" of 1.0:
Stripes
Converting a gradient parameter to "Stripes" adds four sub-parameters:
- color "Color 1"
- color "Color 2"
- integer "Stripe Count"
- real "Width"
The resulting value is a gradient containing "Stripe Count" equally spaced, equally wide stripes of color "Color 2" with a background of "Color 1". "Width" specifies the width of the stripes, with a width of 0 or less meaning they are invisible, and a width of 1 or more meaning the whole gradient is of "Color 2".
Subtract
Converting a parameter to "Subtract" adds three sub-parameters, the first two of which are the same type as the parameter itself:
- <param> "LHS"
- <param> "RHS"
- real "Scalar"
The "Subtract" conversion can be used with parameters of type angle, color, gradient, integer, real, time, and vector.
The resulting value is:
(LHS - RHS) * Scalar
Switch
Converting a parameter to "Switch" adds three sub-parameters:
- <param> "Link Off"
- <param> "Link On"
- bool "Switch"
"Link Off" and "Link On" are the same type as the parameter being converted.
The resulting value is the value of "Link Off" when "Switch" is off, and "Link On" when "Switch" is on.
This conversion can be used on all value types.
Time Loop
Converting a parameter to "Time Loop" adds four sub-parameters: one called "Link", of the same type as the parameter itself, and three time parameters:
- <param> "Link"
- time "Link Time"
- time "Local Time"
- time "Duration"
It works similarly to the Time Loop Layer but affects only a single parameter.
For any integer value n, from "Local Time + abs(Duration)*n" to "Local Time + abs(Duration)*(n+1)", the resulting value of the parameter is the same as that of the "Link" parameter from "Link Time" to "Link Time + Duration".
In other words, "Duration" seconds of values of the parameter "Link" starting from time "Link Time" onwards are looped over and over, with the value of the "Link"ed parameter at time "Link Time" corresponding to the resulting value at time "Local Time".
As an example, suppose the "Link" parameter has a value of time the current time. At 0s the value is 0, at 10s the value is 20.
If we set:
- Link Time = 5s
- Local Time = 2s
- Duration = 4s
then from 2s to 6s and from 6s to 10s, etc., the resulting value is the value of "Link" from 5s to 9s, as follows:
Then the resulting values will be:
- 0s -> "Link" value at 7s = 14
- 1s -> "Link" value at 8s = 16
- 2s -> "Link" value at 5s = 10 (at "Link Time" = 2s, result is the value of "Link" at "Link Time" = 5s = 10)
- 3s -> "Link" value at 6s = 12
- 4s -> "Link" value at 7s = 14
- 5s -> "Link" value at 8s = 16
- 6s -> "Link" value at 5s = 10 ("Duration" = 4s later, the value is the same as at 2s)
- 7s -> "Link" value at 6s = 12
If "Duration" is zero, the resulting value is whatever the value of the "Link" parameter is at time "Link Time".
If "Duration" is negative, the resulting value at "Local Time" still matches the value of "Link" at "Link Time", but the animation goes in the opposite direction. For example:
If we set:
- Link Time = 5s
- Local Time = 2s
- Duration = -4s
then from 2s to 6s and from 6s to 10s, etc., the resulting value is the value of "Link" from 5s to 1s, as follows:
Then the resulting values will be:
- 0s -> "Link" value at 3s = 6
- 1s -> "Link" value at 2s = 4
- 2s -> "Link" value at 5s = 10 (at "Link Time" = 2s, result is the value of "Link" at "Link Time" = 5s = 10)
- 3s -> "Link" value at 4s = 8
- 4s -> "Link" value at 3s = 6
- 5s -> "Link" value at 2s = 4
- 6s -> "Link" value at 5s = 10 (4s later, the value is the same as at "Link Time" = 2s)
- 7s -> "Link" value at 4s = 8
This conversion can be used on all value types.
Time String
Converting a string parameter to "Time String" adds one sub-parameter called "Time", of type time:
- time "Time"
The result is a string containing the given time.
Timed Swap
This convert type was disabled in Synfig 0.61.06 and earlier because it didn't work.
Converting a parameter to "Timed Swap" adds four sub-parameters:
- <param> "Before"
- <param> "After"
- time "Swap Time"
- time "Swap Duration"
"Before" and "After" are the same type as the parameter being converted.
This conversion type linearly switches from "Before" to "After", taking "Swap Duration" seconds to do so, and completing the swap at "Swap Time".
Note that this doesn't give us anything that we can't achieve using the "Linear" conversion type and a few waypoints.
"Timed Swap" can be used on angles, colors, integers, reals, times, and vectors.
The resulting value is:
if time > "Swap Time" then "After"
else if time < ("Swap Time" - "Swap Duration") then "Before"
else interpolate between "Before" and "After"
Two-Tone
Converting a gradient to "Two-Tone" adds two color-valued sub-parameters:
- color "Color1"
- color "Color2"
The resulting gradient has two CPoints, one at each end, starting with "Color1" and ending with "Color2".
These color parameters can be animated, giving us the ability to have the gradient change color over time. This can be used as a workaround for this bug.
Vector Angle
Converting an angle to "Vector Angle" adds a vector sub-parameter:
- vector "Vector"
The resulting value is the angle between the vector and the X axis.
Vector Length
Converting a real to "Vector Length" adds a vector sub-parameter:
- vector "Vector"
The resulting value is the length of the vector.
Vector X
Converting a real to "Vector X" adds a vector sub-parameter:
- vector "Vector"
The resulting value is the X component of the vector.
Vector Y
Converting a real to "Vector Y" adds a vector sub-parameter:
- vector "Vector"
The resulting value is the Y component of the vector.
Which Value Types can use which Convert Types?
There are 13 different types of value in Synfig. Each of these types has a different set of convert types available to it, as follows:
Angle
- Angle parameters can be converted to Add, aTan2, BLine Tangent, Dot Product, Linear, Random, Range, Scale, Step, Subtract, Switch, Time Loop, Timed Swap, Vector Angle, and Reference types.
BLinePoint
- BLinePoint parameters can be converted to Composite, Reverse Tangent, Switch, Time Loop, and Reference types.
Bool
Canvas
Color
- Color parameters can be converted to Add, Composite, Gradient Color, Linear, Radial Composite, Random, Scale, Step, Subtract, Switch, Time Loop, Timed Swap, and Reference types.
Gradient
- Gradient parameters can be converted to Add, Gradient Rotate, Repeat Gradient, Stripes, Subtract, Switch, Time Loop, Two-Tone, and Reference types.
Integer
- Integer parameters can be converted to Add, Linear, Random, Range, Scale, Step, Subtract, Switch, Time Loop, Timed Swap, and Reference types.
List
- List parameters can be converted to BLine, Dynamic List, Switch, Time Loop, and Reference types.
Real
- Real parameters can be converted to Add, BLine Width, Cos, Dot Product, Exponential, Linear, Random, Range, Reciprocal, Scale, Sine, Step, Subtract, Switch, Time Loop, Timed Swap, Vector Length, Vector X, Vector Y, and Reference types.
Segment
String
- String parameters can be converted to the Angle String, Int String, Joined List, Real String, Switch, Time Loop, Time String, and Reference types.
Time
- Time parameters can be converted to the Add, Linear, Random, Range, Scale, Step, Subtract, Switch, Time Loop, Timed Swap, and Reference types.
Vector
- Vector parameters can be converted to Add, BLine Tangent, BLine Vertex, Composite, Linear, Radial Composite, Random, Scale, Segment Tangent, Segment Vertex, Step, Subtract, Switch, Time Loop, Timed Swap, and Reference types.
Compatibility
When a new ValueNode type is added to Synfig, the .sif file format is extended to include a way of writing the new type. This extension won't be able to be read by any older version of Synfig. Here's a list of the ValueNode types that have been added, along with the subversion revision number in which they first appeared:
Version Revision Convert
(0.61.09) not yet released 2010 Int String 2010 Angle String 2007 Joined List 2003 Real String 2000 Time String 1891 Dot Product 1885 Gradient Color 1882 Vector X 1882 Vector Y 1881 Vector Length 1880 Vector Angle
(0.61.08) 1839 1694 BLine Width 1690 Random (for bools) 1691 Step 1354 Subtract (for gradients) 1354 Add (for gradients) 1267 From Integer 1267 Duplicate 1238 Reciprocal 1226 Time Loop 1162 Reverse Tangent 1132 aTan2 1111 Cos 923 Switch 907 Random
(0.61.07) 878 776 Range 744 BLine Vertex 744 BLine Tangent 742 Add 739 Exponential 666 Repeat Gradient 610 Timed Swap
(0.61.06) 536